 Tasks
Tasks
Tasks are the steps within a flow.
Tasks are discrete actions within a flow, capable of taking inputs and variables from the flow and producing outputs for downstream consumption by end users and other tasks.
Flowable Tasks
Kestra orchestrates your flows using Flowable Tasks. These tasks do not perform any heavy computation. Instead, they control the orchestration behavior, allowing you to implement more advanced workflow patterns.
Example Flowable tasks include:
io.kestra.plugin.core.flow.Parallelio.kestra.plugin.core.flow.Switchio.kestra.plugin.core.flow.ForEachItem
Read the full list on the Flowable tasks page.
Runnable Tasks
In Kestra, most data processing workloads are executed using Runnable Tasks.
In contrast to Flowable Tasks, Runnable Tasks are responsible for performing the actual work. For example, file system operations, API calls, database queries, etc. These tasks can be compute-intensive and are handled by workers.
Example runnable tasks include:
io.kestra.plugin.scripts.python.Commandsio.kestra.plugin.core.http.Requestio.kestra.plugin.notifications.slack.SlackExecution
Core task properties
The table below lists the core task properties available to all tasks.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
id | The flow identifier, must be unique inside a flow. |
type | The Java Fully Qualified Class Name of the task |
description | The description of the task |
retry | Task retry behavior |
runIf | To skip the task execution if the provided condition evaluates to false |
timeout | Task timeout expressed in ISO 8601 Durations. |
disabled | Set it to true to disable execution of the task. |
workerGroup.key | To execute this task on a specific Worker Group (EE) |
allowFailure | Boolean flag allowing to the execution to continue even if this task fails. |
allowWarning | Boolean flag allowing to the execution to finish with a SUCCESS state even if this task produces a warning. |
logLevel | Property to define the log level granularity for which logs will be inserted into the backend database. By default, all logs are stored. However, if you restrict that to e.g., the INFO level, all lower log levels such as DEBUG and TRACE won't be persisted. |
logToFile | Boolean flag that lets you store logs as a file in internal storage. That file can be previewed and downloaded from the Logs and Gantt Execution tabs. When set to true, logs aren’t saved in the database, which is useful for tasks that produce a large amount of logs that would otherwise take up too much space. The same property can be set on triggers. |
Dynamic vs. static task properties
Task properties can be static or dynamic. Dynamic task properties can be set using expressions. To find out whether a given task property is static or dynamic, check the task documentation available on the plugin's homepage as well as in the UI when you hover over a task and click on the documentation tab on the right.
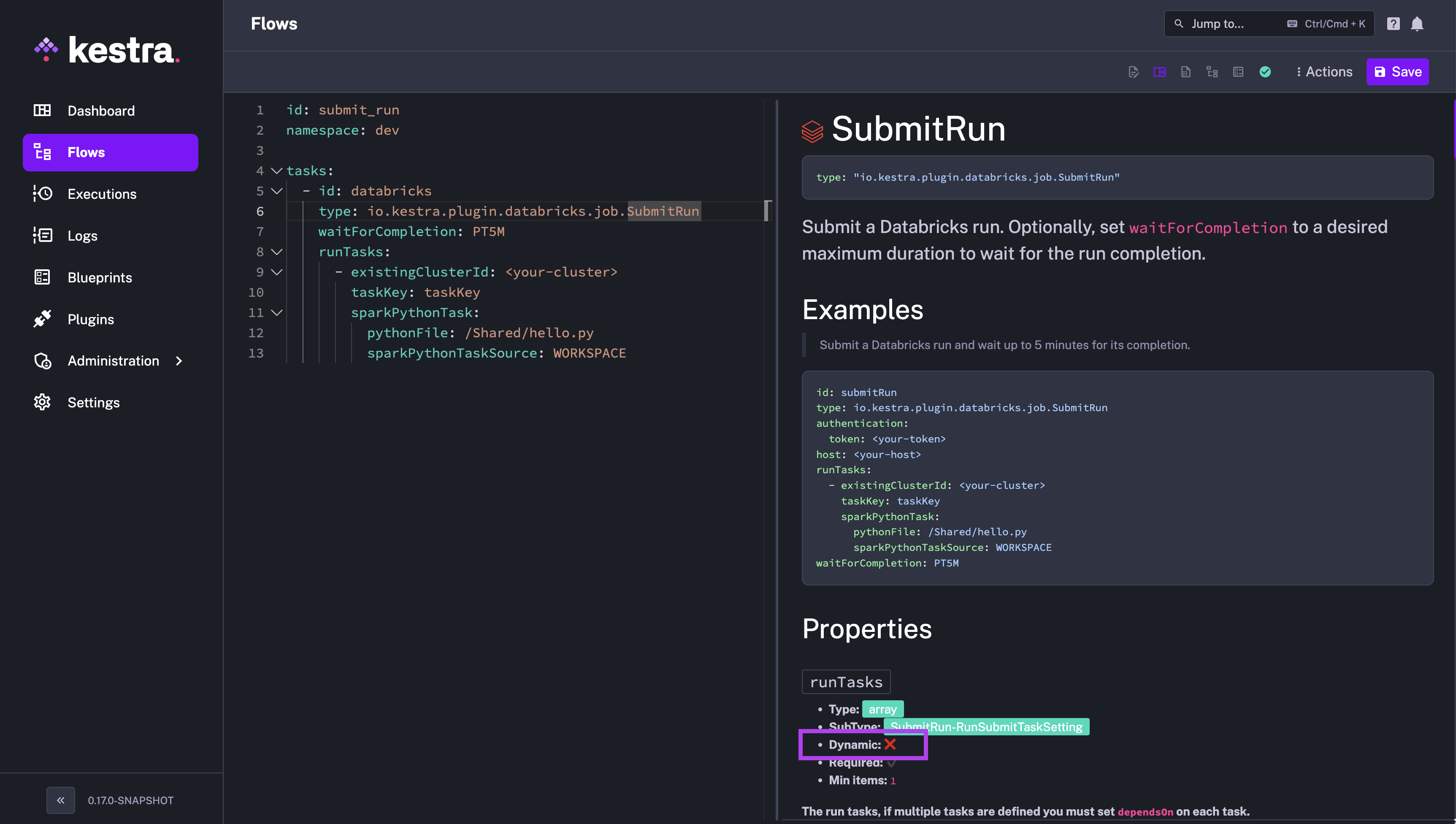
Often some task properties are marked as not dynamic because they are complex types (e.g., maps, list of strings, list of maps), meaning that they are placeholders for other dynamic properties. Let's take the runTasks property of Databrick's SubmitRun task as an example. This property is not dynamic because it's an array of RunSubmitTaskSetting.
On top of that, RunSubmitTaskSetting is a group of other properties which are also either dynamic or of complex type (placeholder for other properties). It's therefore useful to always drill down to the lowest level — most properties at the lowest level are dynamic and can be templated using expressions.
Was this page helpful?